|
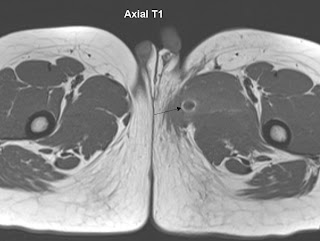
| Axial T1 |
 |
| Axial T2 |
 |
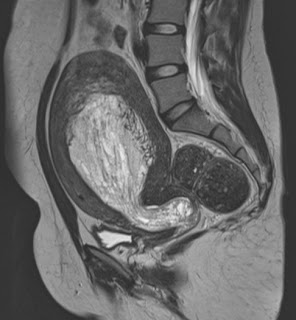
| Coronal T2 |
 |
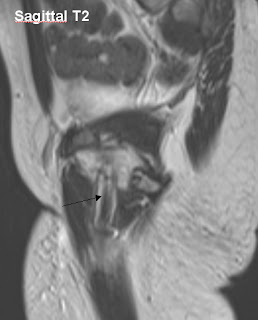
| Sagittal T2 |
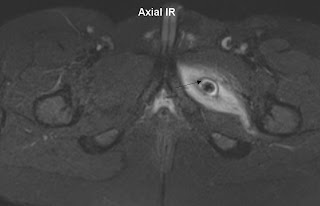
Diffuse hyperintense signal uniform heterogenous thickening of the endometrium on the T2 images that is intermediate signal on T1.
The hyperplasia extends to into the cervical canal bulging through the external os.
This is was histologically proven to be Endometrial hyperplasia.