42 year old man presenting with difficulty in speech and deviation of the tongue to the left. MRI was performed to assess for organic cause.
Axial 3D SPACE
Axial T1
Coronal STIR
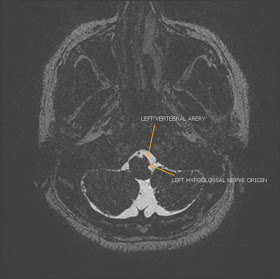
MRI showed a demonstrated a tortuous left vertebral artery compressing the medulla at the emergence of the left hypoglossal nerve rootlets.
On the coronal STIR images there is atrophy of the left half of the tongue which appears reduced in bulk and minimally hyperintense compared to the right.
Microvascular decompression of the vertebral artery can result in resolution of the nerve palsy.
Axial 3D SPACE
Axial T1
Coronal STIR
MRI showed a demonstrated a tortuous left vertebral artery compressing the medulla at the emergence of the left hypoglossal nerve rootlets.
On the coronal STIR images there is atrophy of the left half of the tongue which appears reduced in bulk and minimally hyperintense compared to the right.
Microvascular decompression of the vertebral artery can result in resolution of the nerve palsy.